
Master Python Programming with Us!
Join our comprehensive course and become proficient in Python for web development, data science, automation, and more.

Learn Python in 2025: Your Gateway to a Future-Proof Tech Career
Python remains one of the most in-demand programming languages in the world—and for good reason. Whether you're stepping into tech for the first time or looking to level up your skills, Python offers versatility, simplicity, and powerful career opportunities.
-
Beginner-Friendly
Clean and easy-to-read syntax makes Python the ideal first language.
-
Versatile Applications
From web development to automation, data science to AI, Python powers it all.
-
High Demand
Python developers are some of the most sought-after professionals across industries.

Master Python with Real-World Experience
Our industry-driven Python course is perfect for beginners and professionals alike. Build strong foundations in programming, data analysis, and automation.
- Real-world projects: automation scripts, web apps, dashboards
- Job-ready skills in Data Science, AI/ML, and Web Dev
- Mentorship, certification & portfolio-worthy projects

No Coding Experience? No Problem!
Learn Python from scratch with beginner-friendly content and interactive challenges that help you become confident fast.
- Easy-to-follow modules & real exercises
- Collaborative learning & community support
- Tech-career-ready skillset
Course Syllabus Overview
This is a brief overview of the syllabus. For more detailed information on each topic, please download the full syllabus.
Download Full SyllabusModule 1: Getting Started with Python
1.1: Introduction to Python
Why Python is the language of choice for modern developers.
1.2: Setting Up Python
Installation, IDEs, and Python shell.
1.3: Writing and Running Scripts
Hello World and basic syntax.
1.4: Comments and Documentation
Inline and docstring documentation.
1.5: User Input and CLI Arguments
Handling basic I/O and arguments.
Module 2: Core Python Data Structures
2.1: Primitive Data Types
Strings, numbers, booleans.
2.2: Variables and Memory
Variable binding and scope.
2.3: Control Flow
If-else, loops, and logical operators.
2.4: Built-in Functions
Common built-ins like `len`, `type`, `range`, and `input`.
2.5: Type Casting and Conversion
Converting between strings, ints, floats.
Module 3: Advanced Data Structures
3.1: Lists and Tuples
Indexing, slicing, methods.
3.2: Dictionaries and Sets
Key-value pairs and unique collections.
3.3: Comprehensions
Create lists, sets, and dicts concisely.
3.4: Iterators and Generators
Lazy evaluation with `yield` and iterables.
Module 4: File I/O and Persistence
4.1: Reading/Writing Text Files
File modes, paths, and file objects.
4.2: Binary Files and Appending
Append mode and working with binary streams.
4.3: Serialization with JSON & CSV
Save and load structured data with `json` and `csv` modules.
Module 5: Functions and Modularization
5.1: Defining Functions
Parameters, arguments, return values.
5.2: Lambda Functions
Anonymous functions and use cases.
5.3: Modules and Packages
Importing, creating, and organizing code into packages.
Module 6: Object-Oriented Programming
6.1: Classes and Objects
Creating objects and constructors.
6.2: Encapsulation and `self`
Object state and behavior.
6.3: Inheritance and Polymorphism
Reusability and method overriding.
6.4: Abstract Classes and Interfaces
Design patterns and `abc` module.
Module 7: Error Handling & Regex
7.1: Exception Handling
Try, except, finally, raising errors.
7.2: Regular Expressions
Match patterns with `re` module.
7.3: Validating Inputs
Use regex to clean and validate data.
Module 8: Multithreading & Concurrency
8.1: Working with Threads
Basic threading with `threading` module.
8.2: Thread vs. Process
Differences and appropriate use cases.
8.3: Synchronization
Locks, race conditions, and thread safety.
Module 9: Databases and SQL
9.1: Connecting to MySQL
Set up and connect with `mysql.connector`.
9.2: CRUD Operations
Create, Read, Update, and Delete in SQL.
9.3: Parameterized Queries
Secure and dynamic data access.
Module 10: Final Project
10.1: Project Planning
Define scope, goals, and structure.
10.2: Building Your Application
Implement concepts in a capstone project.
10.3: Testing and Deployment
Debug and publish your application.
Course Conclusion
Wrap-Up and Q&A
Review key concepts and clarify doubts.
Certification
Receive your course completion certificate.
Next Steps
Get resources for advanced learning and career paths.
Learning Support & Career Services
Enhance your learning with real-time help, regular assessments, and expert career guidance.
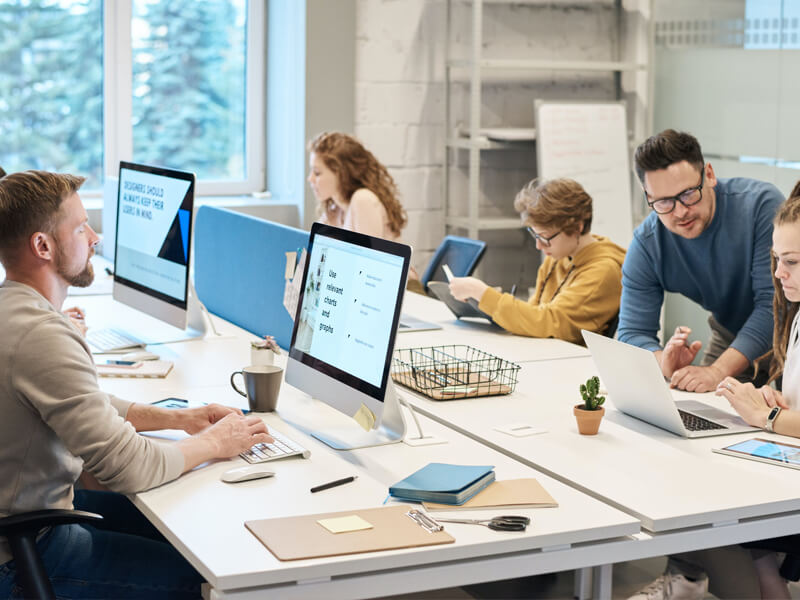

Live Doubt-Solving Sessions
Attend live Q&A and mentoring sessions to clarify your doubts in real time.
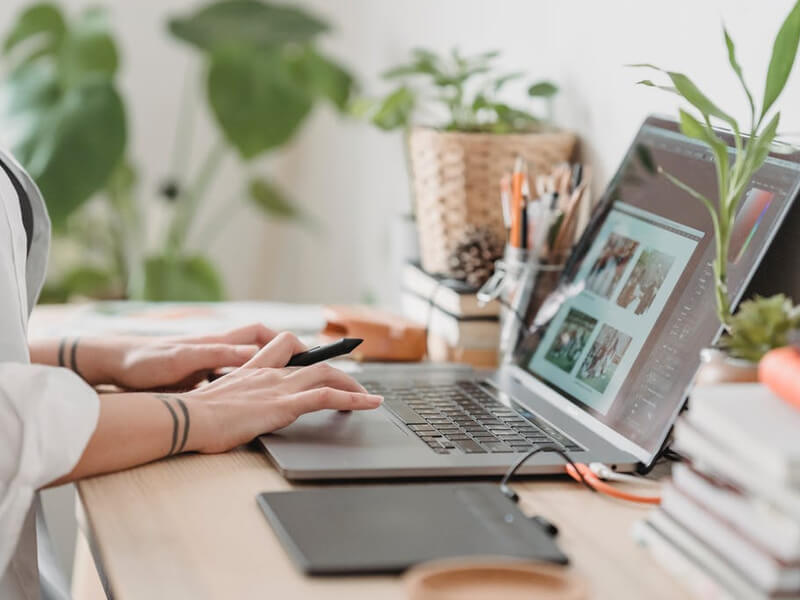

Assignments & Weekly Tests
Regular assessments to track your progress and reinforce learning.
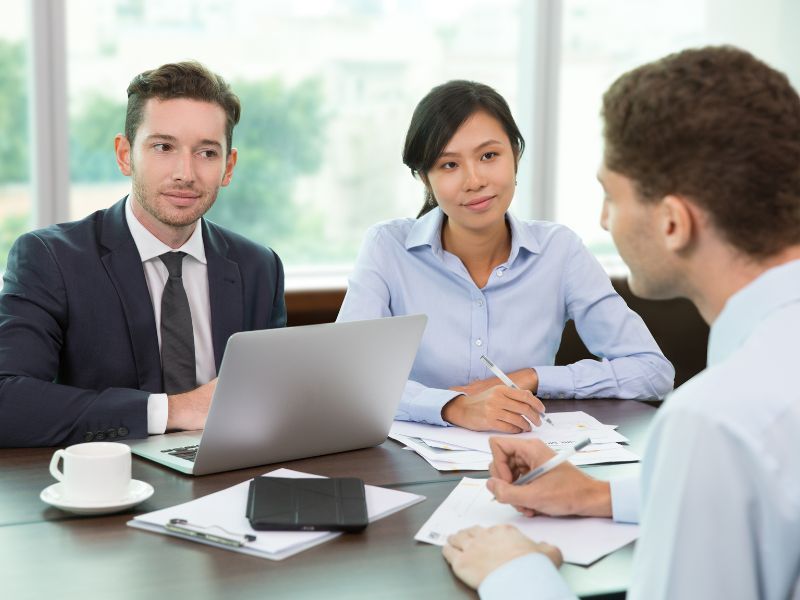

Interview & Career Preparation
Personalized mock interviews, coding interview practice, and resume-building tips.
💥 Limited-Time Discounts on Tech Courses!
Grab your spot and save big on the skills that matter.
🎓 School Student Deal – 30% OFF
Get 30% off beginner-friendly coding, web, and STEM courses! Start your tech journey today.
Get Offer🏫 College Exclusive – 25% OFF
Advance your tech skills with 25% off specialized software and data courses built for college students.
Claim Deal👥 Group Deal – Save up to 40%
Join with 3+ friends and unlock up to 40% in savings! Study together, succeed together.
Join Now⚡ Flash Sale – 50% OFF (24 Hrs!)
Enjoy a massive 50% off any course for the next 24 hours. Don’t miss out!
Special offerPython Interview Questions
Prepare for your next technical interview with commonly asked Python questions, covering topics from basic syntax to advanced concepts.
>Conceptual Interview Questions:
1.1: What is Python, and how does it differ from other programming languages?
1.2: Explain the difference between Python 2 and Python 3.
1.3: What are Python's unique features?
1.4: What are identifiers vs. keywords?
1.5: Why is indentation important?
Programming Questions:
1. Write a program to print "Hello, World!"
2. Check if a number is even or odd
Conceptual Interview Questions:
2.1: What is the difference between a list and a tuple in Python?
2.2: What are the different data types in Python? How are they different from each other?
2.3: Explain how Python’s memory management works with objects.
2.4: What are the advantages and disadvantages of using dictionaries in Python?
2.5: What is the difference between `deep copy` and `shallow copy`?
Programming Questions:
1. Write a Python program to reverse a list without using the reverse() method.
2. Write a Python program that counts the frequency of each element in a list.
Conceptual Interview Questions:
3.1: What are `break`, `continue`, and `pass` statements used for in Python?
3.2: What is the difference between `is` and `==` in Python?
3.3: Explain how `for` loops and `while` loops differ in Python.
3.4: What are the different types of functions in Python?
3.5: How do lambda functions work in Python?
Programming Questions:
1. Write a Python program to check if a given number is prime or not.
2. Write a Python function that accepts a string and returns it in reverse order.
Conceptual Interview Questions:
4.1: How can you open and read a text file in Python?
4.2: What is the purpose of the `with open()` statement in Python?
4.3: What is the difference between `read()` and `readline()` in Python when working with files?
4.4: What are the different file modes in Python?
Programming Questions:
1. Write a Python program to read a text file and count the number of words in it.
2. Write a Python program to copy the contents of one file to another.
Conceptual Interview Questions:
5.1: What is object-oriented programming (OOP)? Explain the four pillars of OOP.
5.2: What is inheritance in Python, and how does it work?
5.3: What is polymorphism in Python? Give an example.
5.4: What is the role of the `self` keyword in Python classes?
5.5: How does Python handle multiple inheritance? What are the potential issues?
Programming Questions:
1. Write a Python class that represents a rectangle. The class should have methods to calculate the area and perimeter.
2. Write a Python class that implements a basic bank account with methods to deposit and withdraw money.
Conceptual Interview Questions:
6.1: What is the difference between `try`, `except`, `finally`, and `else` in Python’s exception handling?
6.2: Explain how Python’s exception hierarchy works.
6.3: What are regular expressions, and how are they used in Python?
6.4: What is the `re` module in Python?
Programming Questions:
1. Write a Python program that handles exceptions when dividing two numbers, and ensures that the denominator is not zero.
2. Write a Python program to find all the email addresses in a given text using regular expressions.
Conceptual Interview Questions:
7.1: What is multithreading, and how does Python handle it?
7.2: What is the Global Interpreter Lock (GIL), and how does it affect Python's multithreading?
7.3: What are some common problems with multithreading, and how can they be solved?
7.4: How do you synchronize threads in Python?
Programming Questions:
1. Write a Python program that prints "Hello from Thread 1" and "Hello from Thread 2" using multithreading.
2. Write a Python program that calculates the factorial of a number using threads.
Conceptual Interview Questions:
8.1: How do you connect Python to a MySQL database?
8.2: What is the difference between DML and DDL operations in SQL?
8.3: What is an SQL injection, and how can it be prevented in Python?
8.4: How can you handle database errors in Python?
Programming Questions:
1. Write a Python program to connect to a MySQL database and retrieve all rows from a table.
2. Write a Python program to insert a new record into a database using Python and MySQL.
Conceptual Interview Questions:
9.1: What is a Python decorator, and how does it work?
9.2: What is a generator in Python, and how does the `yield` keyword function?
9.3: How does the `map()` function work in Python?
9.4: What are Python's built-in higher-order functions, like `filter()` and `reduce()`?
Programming Questions:
1. Write a Python generator function to generate Fibonacci numbers up to a given limit.
2. Write a Python decorator that logs the function name and arguments whenever a function is called.
Conceptual Interview Questions:
10.1: How would you approach debugging a Python application that is performing slower than expected?
10.2: How would you optimize a Python application that is consuming too much memory?
Programming Questions:
1. Build a Python application that performs CRUD operations on a database.
2. Build a Python web scraper that extracts headlines from a news website.
Python Project Ideas
A collection of simple, fun, and practical projects to enhance your core Python programming skills.

Simple Calculator
A lightweight, command-line calculator.Build a basic calculator that performs arithmetic operations using only core Python functionality.

Number Guessing Game
Fun interactive game to test your skills.Create a game where the player guesses a randomly selected number with hints after each try.
To-Do List Manager
Manage tasks efficiently with Python.Develop a command-line to-do list program where users can add, remove, and view tasks.
Simple Chatbot
A rule-based chatbot for fun interaction.Create a Python program that can respond to basic user queries using predefined rules.
Text-based File Organizer
Automatically organize files by type.Create a script that sorts files into folders based on their extensions using core Python tools.

Basic Contact Book
Store and manage contacts easily.Create a command-line system for adding, searching, updating, and deleting contact records.
